“Parallel Currents Attract”
“Anti-Parallel Currents Repel”
The mathematical equations from Ampere’s Law show that the trajectory of motion of electromagnetism around a conductor is Helical in nature. The 2 basic motions are described, with each propagation manifesting into Laws of physics.
Helicity of particle physics is used to describe waves of motion that have equal and opposite components. This means a double helical wave with 2 opposite peaks attract each other to their common central axis and do not expand inversely with distance in the direction of travel along the Z-axis if velocity is maintained.
Cyclotron motion is associated with Fibonacci sequence and is used to describe waves of motion that are of single peak in nature and thus expands inversely as it propagates along its axis. Commonly known as the Inverse Square Law
Chirality is the enantiomer of helical motion, ie. The mirror image of rotation in the direction of travel. Observers with the mirrored perspective of the same helical motion will view the opposite value. Ie; Positive is Negative, North is South, Spin up is Spin down, Clockwise is Anti-clockwise.
The illustration of 2 parallel conductors show us that Coulomb’s Law manifests when 2 identical waves travel in the same direction. Since a central observer between both waves must rotate his perspective to view each conductor and thus views spin up to his left and spin down to his right the 2 conductors attract each other when current flows.
Parallel Rotation of the Poloidal Axis of the Atomic wave function
Atoms of all shapes and sizes produce what has been commonly referred to as electron shells, which is the simplest 2D perspective of a 3D object. Advancing to a 3D perspective we call the shells electron clouds and electron orbitals that form the Schrödinger Wave Equation of Quantum Mechanics.
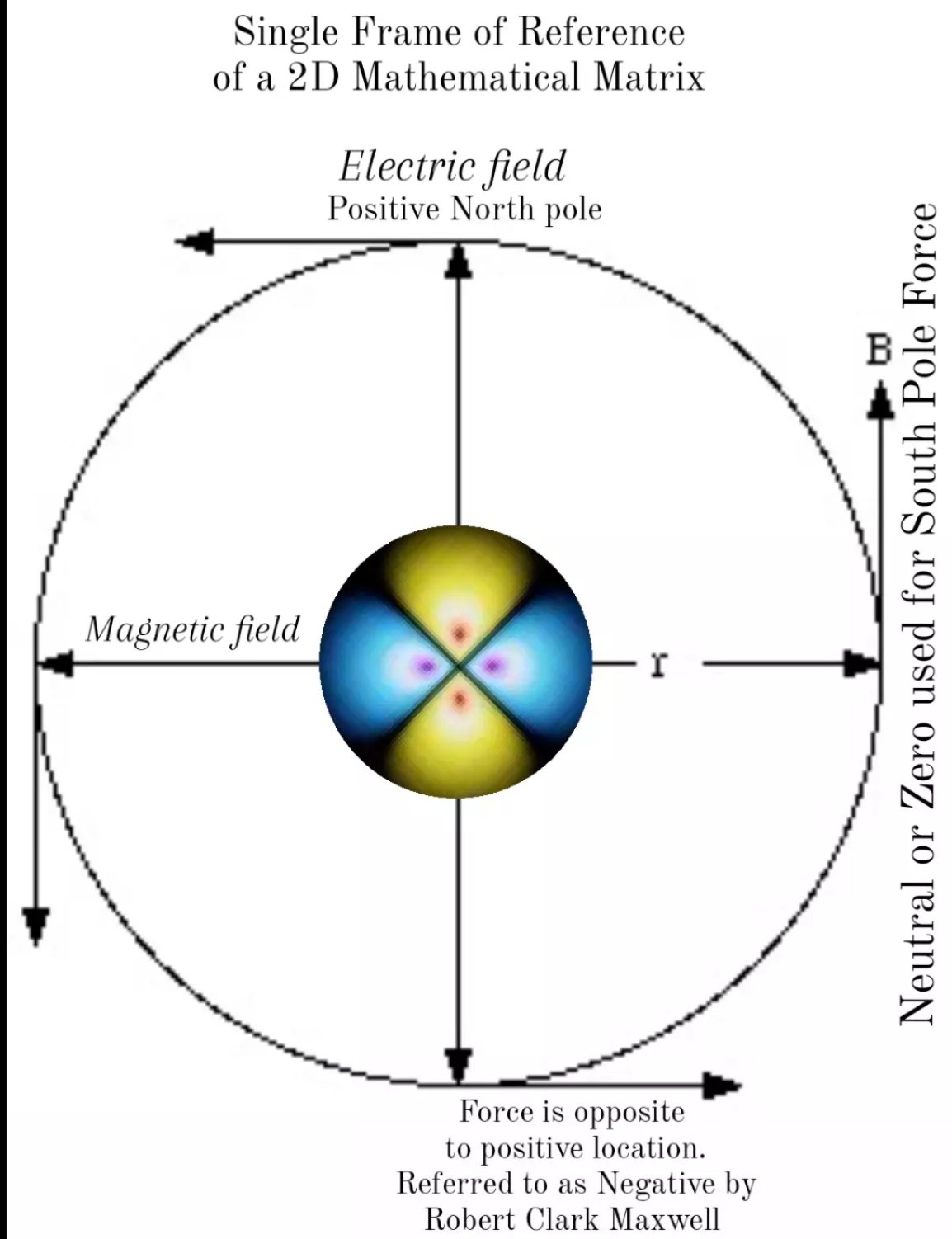
Each orbital forms a quadrant of the overall Quadrupole when viewed from the poloidal perspective, which then forms the dipole from the Equatorial perspective. The outside of each electron shell rotates in the same direction to any equatorial frame of reference.
“It is convenient to switch from Cartesian coordinates to spherical coordinates in terms of a radius r, as well as angles ϕ, which is measured from the positive x axis in the xy plane and may be between 0 and 2π, and θ, which is measured from the positive z axis towards the xy plane and may be between 0 and π“.
Since electromagnetic waves exists in a 3 dimensional universe we must lose the 2D understanding of magnetic field lines and progress to 3D magnetospheres and Helical wave functions. Thankfully this is not complicated and in fact the math has already been done for us by Schrödinger. The only thing left to do is apply the correct coordinate system to electromagnetic waves such as Light, Electricity, Magnetism and Gravity. Unification of all forces is simple when we remove the negative value of an electromagnetic wave with an equal but opposite value. This must be done because when we reverse any wave in 3 dimensions the opposite value is no longer opposite. This effect can be understood by rotating a spherical object in front of a Mirror.
Orbital Nodes
“What is a Node?
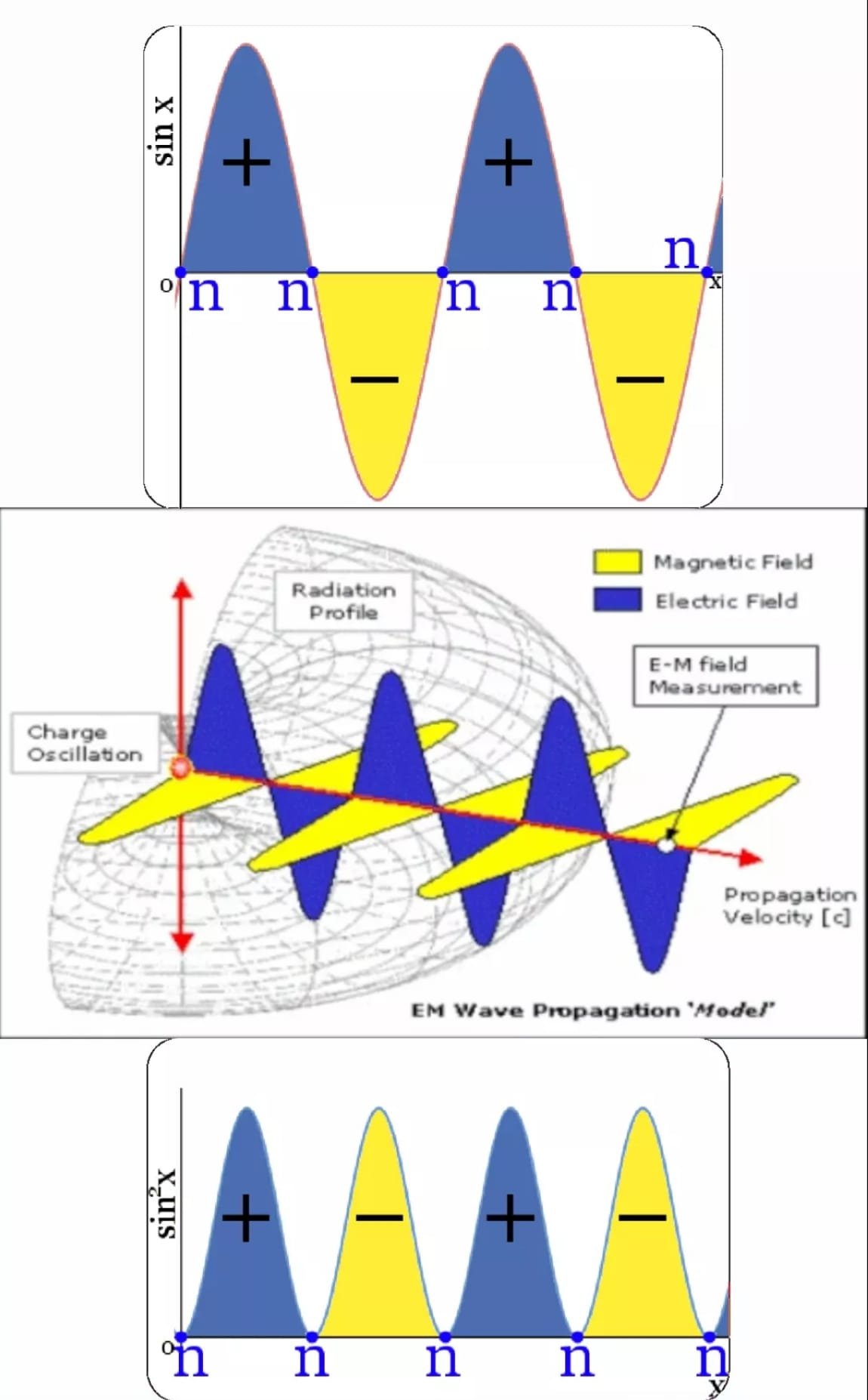
Consider the sine function sin x as a simple wave function Ψ. The diagram below shows:
when sin x is greater than zero, the phase of the wave is positive
when sin x is less than zero, the phase of the wave is negative
when sin x is zero, the point is described as a node”
From the above Quoted statement linked on the image, we can see that the Negative value comes from the fact the wave is below the axis as orientated to a single observer. If that observer was rotated 180* around either axis (his own axis or the waves) the values must change sign from positive to negative, since “above” and “below” have changed to his orientation.
“sin2 x has identical nodes to sin x
the value of sin2 x has no negative values
where the phase of Ψ was positive the phase of Ψ2 is still positive
where the phase of Ψ was negative the phase of Ψ2 is still negative
nodes separate positive and negative phases”
Now we look at the same Wave Measured from the point source in 3 dimensional space and we see that the negative value of the wave disappears. The Equal value between both waves is still visible however the negative value is now above the axis, this is due to the opposite rotation (chirality)of the wave. The definition of Negative has changed from a location below the measured axis to a phase, clearly this is 2 different measurement scales and has not been accounted for in the mathematical framework.
The central observer (Theta) between the same wave travelling in both directions (such as an electrical coil) acts like a Bridge Rectifier to the Electromagnetic Helical wave.
Quantum Nodes
Equal and Opposite - Opposite and Negative are equally measured in the 2D mathematical framework and this needs to be rectified in order to unify all the forces since it is not true in our 3D reality as shown by the terminology being change to “phase”.
Notice the Flip in Phase as the wave heads outward either side of the nodes. The opposite observer must see the phase reversed due to his orientation changing to the waves rotational direction.
Schrödinger's Cat
The famous thought experiment proposed by Edwin Schrödinger's has only 2 possible states. Since all 3D wave function’s actual have 3 possible states. These being “Positive” spin up phase, “negative” spin down Phase and the deconstructive Node phase.
Therefore the answer to the thought experiment is that the cat is sleeping during the Node Phase, during the spin up “positive” phase the cat is having his belly rubbed and purring like a nice little kitten and the opposite phase called the spin down “Negative” phase the Cats mode (mood) has turned and he has decided your arm is no longer welcome in his box.
Another easier to visualise example would be a spinning coin between 2 observers. The first observer must always view the opposite of the second observer, except when the edge (Node) of the coin faces both observers.